- October 20, 2023
- Posted by: M. Sadegh Riasi
- Category: Research News
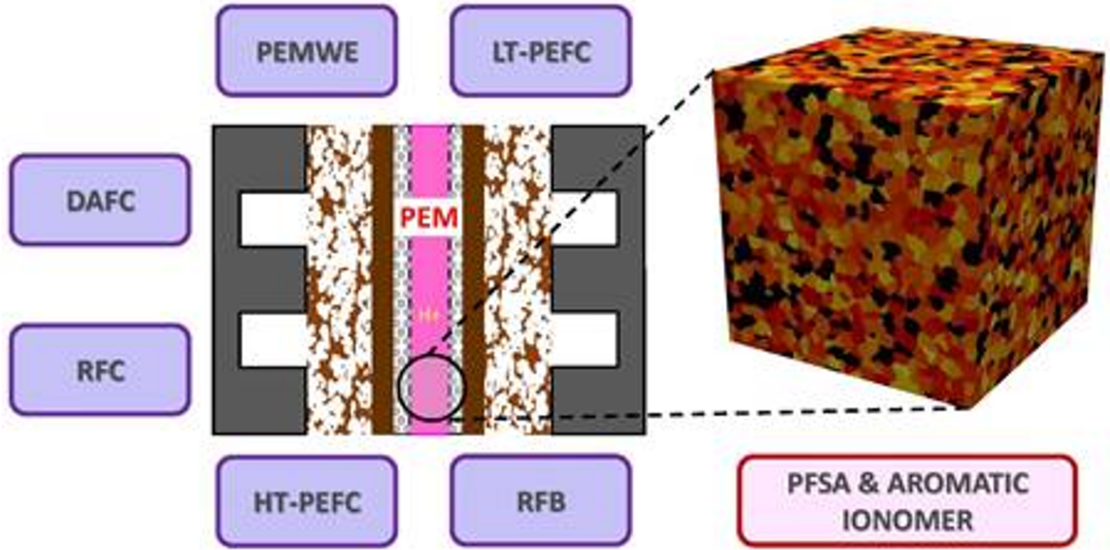
Proton Exchange Membranes for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells: An Analysis of Perfluorosulfonic Acid and Aromatic Hydrocarbon Ionomers
Pablo A. García-Salaberri
Ionomers can be classified into two main groups: (i) perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) polymers, and (ii) aromatic hydrocarbon (HC) polymers. In this work, an analysis of key characteristics of both PEM types is presented, including water uptake, proton conductivity, water transport properties, thermal conductivity, permeability, mechanical properties and chemical and thermal stability, among others. Comparatively, PFSA-based PEMs are undoubtedly the commercial standard due to its proven high proton conductivity and good chemical stability, even though reinforced aromatic HC-based PEMs have also started to be commercialized recently. In the last decades, a growing trend is identified toward the development of hybrid and composite ultra-thin PEMs (5–20 μm in thickness) with tailored properties.
Sustainable Materials and Technologies, Volume 38, December 2023, e00727
Corresponding Author: Pablo A. García-Salaberri
InterPore Members can promote their publications to the community via the InterPore InJournals Section of the Newsletter. If you wish to do so, please submit your publication highlight to newsletter@InterPore.org. Clearly indicate which of the authors is an InterPore member (or the institute with an Institutional Membership). Note that we will not review the entries nor does InterPore endorse the published work. Furthermore, we publish on a “submitted first, published first” basis. The highlighted publication should be no older than 6 months (available online).
The highlight should be short (max 100 words) and contain an illustration. Please note that we offer this opportunity exclusively to InterPore members. If you would like to become a member, please have a look here.

