- December 23, 2023
- Posted by: M. Sadegh Riasi
- Category: Research News
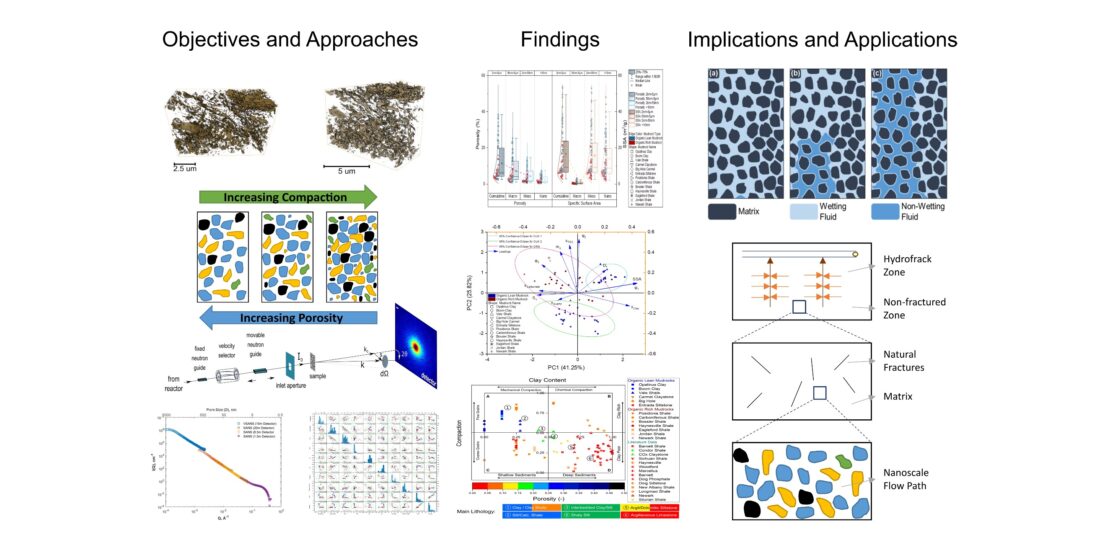
A. Rezaeyan, N. Kampman, V. Pipich, L. C. Barnsley, G. Rother, C. Magill, J. Ma, A. Busch
Mudrocks, ubiquitous yet poorly understood sedimentary rocks with significant variations in pore structure, form seals for geological carbon dioxide and energy storage, repositories for radioactive waste disposal, and reservoirs for natural gas. With a combination of small angle neutron scattering measurements and multivariate statistical analyses on a unique set of mudrock samples, we show that compaction is the primary and clay the secondary control on mudrock porosity. While TOC barely affects mudrock porosity, it influences meso- and macropores the most. Mudrock controls influence porosity and subsequent flow differently across various scales, affecting storage or production capacity in mudrocks.
Energy, 289, February 2024, 129966
Corresponding Author: Amirsaman Rezaeyan
InterPore Members can promote their publications to the community via the InterPore InJournals Section of the Newsletter. If you wish to do so, please submit your publication highlight to newsletter@InterPore.org. Clearly indicate which of the authors is an InterPore member (or the institute with an Institutional Membership). Note that we will not review the entries nor does InterPore endorse the published work. Furthermore, we publish on a “submitted first, published first” basis. The highlighted publication should be no older than 6 months (available online).
The highlight should be short (max 100 words) and contain an illustration. Please note that we offer this opportunity exclusively to InterPore members. If you would like to become a member, please have a look here.

